Accounting vs Bookkeeping: Key Differences for Business Success
Every business community needs a certified public accountant to check the business's financial health amid the wicked corporate world and the highly competitive economic environment of Ghana. These two terms, accounting and bookkeeping, are often misunderstood by business owners, and yet they are the mainstays of the business. At the same time, these two terms are the determining factors of the business's success or failure. Although both of them are crucial in the activities of the business in Ghana, they are like counterparts; they have different roles in profit-making and compliance areas. You may think that the two descriptions are the same, but in reality, they are not only different, but they are not even close. This guide is going to teach you the difference between accounting and bookkeeping, one versus the other, thus making you the present financial situation master of your business which will result in a better and stronger financial foundation. For businesses looking to streamline financial operations further, exploring IPMC's suite of software solutions can be a great starting point.
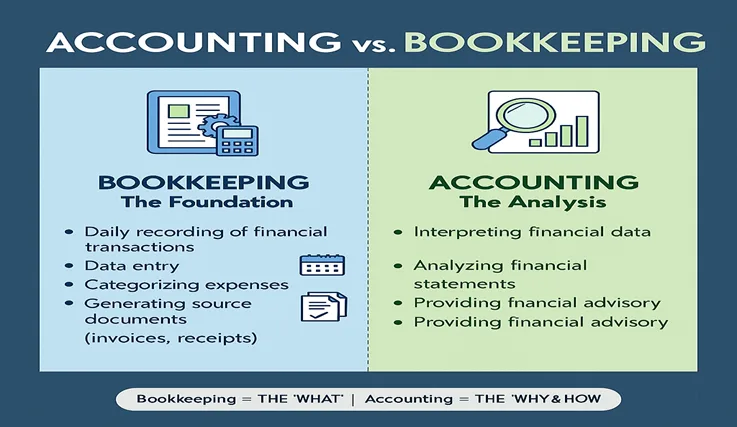
What Is Bookkeeping? The Foundation of Financial Data
Bookkeeping can be best described in one's mind as the systematic approach of recording the daily financial activities of a business. It is the preliminary layer, the careful accumulation of raw financial data. The bookkeeper has the task of making sure that each transaction, every cedi that comes in and every cedi that goes out, is correctly logged and classified. This method generates the initial proof of your company's financial transactions. For any business with a bookkeeping practice in Ghana, this function marks the beginning of all the financial analyses that will follow.
The primary aim of bookkeeping is to maintain a continuous and accurate record of all financial transactions. It implies performing a series of tasks that are robotic but very crucial, which together form the foundation of accounting. Accurate bookkeeping is necessary for all financial activities; otherwise, a financial analyst would be like someone trying to build a house on a hillside made of sand, unstable and unreliable.
Tracking Daily Financial Transactions: The Core of Bookkeeping
Diligently tracking daily financial activities is the main function of bookkeeping. An administrative and procedural function that requires a great deal of accuracy and caretaking is the one defined by the core of bookkeeping. The major activities involved in this are:
- Recording Transactions: Every sale, purchase, payment, and receipt is logged into the company's ledgers or accounting software step by step.
- Managing Accounts Receivable and Payable: Money owing to the business is being tracked (invoices sent to customers), and money the business owes suppliers (bills received).
- Performing Bank Reconciliations: The reconciliation process entails matching the internal financial statements of the company with the bank statements issued and finding the discrepancies.
- Invoice Generation and Payroll Processing: This would involve the billing and sending of receipts to customers, and also ensuring payroll for employees is processed correctly and timely. Automation through software, such as TallyPrime, helps streamline these tasks efficiently.
- General Ledger Maintenance: The general ledger is the ultimate record that showcases all transactions by each account in a summarized manner.
In short, the bookkeeping method answers the question: “What financial transactions happened, and when?” It is all about entering and arranging data, as well as supplying the raw, factual numbers that depict the story of the daily operations of a business.
What Is Accounting? Interpreting the Financial Story
If bookkeeping contains the fragments of a puzzle, accounting is then about making the fragments visible and seeing the whole picture. Accounting is a process of a subjective nature that is executed at a high level and takes the steps of analyzing, interpreting, and summarizing the financial data which are prepared by the bookkeeper. It changes the data of mere numbers into information of great significance that can be utilized by business owners, investors, and regulators to make the right decisions based on the knowledge they have.
An accountant takes the ledgers and statements that the bookkeeper has prepared and works with them to produce reports, simulate future scenarios, and give strategic insights. This role is less about documenting the past and more about grasping what that past means for the future of the business. For total financial management in Ghana, accounting is the strategic engine that promotes the growth and sustainability of the business. Companies often integrate accounting with broader enterprise solutions, such as ERP systems, to support holistic business management.
Analyzing and Interpreting Financial Data: The Strategic Role of Accounting
Accounting is, by its very nature, an analytical and consulting operation. It extends from the mere recording of the facts ('the what') into the critical questioning, 'why', and 'what next'. The accountant is responsible for performing tasks of a paramount nature that will have a great impact on the business strategy, including:
- Preparing Adjusting Entries: The accrual basis of accounting requires entries for revenue that has been earned but not yet recorded, as well as expenses that have been incurred but not yet recorded, thereby ensuring that the financial statements accurately report the company's financial position.
- Creating Financial Statements: The accountant is in charge of making the three principal reports – the Income Statement (Profit & Loss), Balance Sheet, and Statement of Cash Flows, which briefly address the company's performance and financial situation.
- Conducting Financial Analysis: The accountant makes comparisons of the financial statements among the different ratios (e.g., profitability, liquidity, debt ratios) to decide on the health, performance, and trends of the company.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: It is the process of using historical information to prepare budgets for the future as well as predict upcoming revenues, expenses, and cash flows.
- Tax Planning and Filing: It is the process of providing tax strategies to various types of taxes to minimize the tax liability and preparing official tax returns and other related government tax reports.
- Providing Strategic Advice: In relation to the accounting methods, that itself the strategic queries: "Is the business really making a profit?“, and also “Do we have enough cash for expansion?" as well as "Which one of the cost categories is most huge?”.
Accounting so answers strategic questions like: "Is the business profitable?", "Do we have enough cash to expand?", and "What are our biggest cost drivers?".
Major Differences Between Accounting and Bookkeeping
Despite being closely tied to one another, bookkeeping and accounting are different phases of the financial management process. Knowing the difference between them is important for efficient resource allocation in your company. One of the main points of disagreement between accounting and bookkeeping is whether they differ in the objectives, practical knowledge needed, as well as the tools that are used.
Roles, Responsibilities, and Tools: A Detailed Comparison
The following section presents the major differences in detail:
- Objective and Focus:
- Bookkeeping is essentially mechanical and bureaucratic. It mainly aims at the accurate and systematic recording of financial data. The focus is on the past and the present, that is, recording the events that have taken place.
- Accounting is essentially personalized and directive. The main objective is to interpret data, ascertain the financial position of the business, and thus direct/control the future decisions thereof. The focus is on the present and future, that is, the use of past data to follow a course ahead.
- Decision-Making:
- Bookkeeping, at first, does not provide the directly involved data for making business decisions. It stands for what is called the input data for making judgments, but it is not the duty of a bookkeeper to perform analysis or provide information at the same time.
- Accounting is primarily responsible for making decisions to be made possible. The statements and advice of accountants are made to business owners and managers to allow them to have an overall view of their operations, investments, growth, and to make strategic choices as per that view.
- Skills and Qualifications:
- Bookkeeping demands no more than a high school diploma or, in some cases, an associate's degree. To perform well in bookkeeping, one has to have the best qualities in organizational skills, attention to detail, and be competent at using bookkeeping software. The only time when a certificate, such as Certified Bookkeeper, is indispensable is when it enhances the standing of an employee, and is not obligatory.
- For accounting, a well-rounded degree in accounting or, otherwise, finance is the norm. But for some advanced positions and some specific responsibilities, such as auditing and signing off on the financial statements, professional qualifications like becoming a Chartered Accountant (CA) or Certified Public Accountant (CPA) are very much a must. The level of skills required is to be analytically very, very strong, interpreters with an advisory nature.
- Tools of the Trade:
- The tools of bookkeeping are mainly the instruments used for recording data. These are paper books (which are no longer popular), electronic spreadsheets, and bookkeeping software apps. The primary goal is to have the data entered and arranged most efficiently.
- Accounting tools are directed towards the process of analysis and reporting. Accountants do their work by using the data generated by bookkeeping software companies, but at the same time, they employ very extensive analytics tools, such as financial modeling that is complex in spreadsheets (Excel) and sophisticated software for tax preparation and financial forecasting.
- Output and Deliverables:
- The bookkeeping function gives out the main records first: the general ledger, trial balance (a report that checks the arithmetic accuracy of the books), and the accounts payable and accounts receivable balances.
- Accounting gives out the high-level financial statements (Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow Statement), analytical reports, tax returns, and audit opinions.
The Synergistic Relationship
It is crucial to look at these functions not as isolated areas but as related to each other. Competent bookkeeping is the very basis of meaningful accounting. If there are errors in the data provided in the bookkeeping process, the accountant's subsequent analysis and reports will be misleading, and could very well lead to possibly business disaster. In the case of financial services providers in Ghana who want excellence, both exercises should be executed with the same care and faithfulness. Those interested in enhancing their business systems can consider further solutions like the ones offered on RapTech.
Which Function Does Your Business in Ghana Need?
The answer would be "Both" in most circumstances. The requirements and strategies for managing them are to be tailored to the business organization's size and the complexity of its operations.
- Startups and Small Businesses: A one-man show, who could be the business owner or a part-time bookkeeper, might be in charge of the bookkeeping. With the growth of the business, they might decide to hire an external accountant to do a quarterly or annual check to secure the records, prepare financial statements, and deal with tax filing operations.
- Growing and Medium-Sized Business: As the company grows, the task of managing transactions every day is mainly given to the in-house bookkeeper, who works hourly. The more complex reporting, analysis, and planning are covered by the firm on a higher level, where the money, in this case, is always found. Considering integration with inventory and financial tools can be valuable; take a look at the best inventory software in Ghana to optimize stock alongside accounting.
- For huge, existing companies, separate departments are dealing with financial operations and managerial accounting. An example of such a big finance department would be one having 'bookkeepers' or 'accounting clerks' as team leaders, who report to staff accountants. The staff accountants will then report to the accountant in charge of managerial and strategic issues, such as the Controller or the Chief Financial Officer (CFO).
Conclusion: Laying a Financially Healthy Foundation for Ghana
The distinction between accounting vs bookkeeping is a major step to be taken in the journey of business growth. Bookkeeping is the diligent recording of your financial past, while accounting is the art and science of molding your future with the aid of that past. One cannot do well without the other.
For the ones in Ghana and pointedly working on the area of money management perfection, it is not an expense to acquire both proper bookkeeping in Ghana and suitable accounting services; with this investment, the company attains clarity, obeys the standards, and remains the leader in the market. To explore suitable software and professional services, check out where to buy accounting software in Ghana or IPMC's eBiz services. Through the creation of a robust bookkeeping structure to be the source of the data-driven decisions and the adoption of the accounting analysis of the experts, a company can be able to face the twists and turns of the Ghanaian market. They can be confident enough to make data-driven decisions, and at the same time, they can build a long-lasting success story. For direct assistance or consultation, please contact us.